Fraunhofer FEP optimises production process for metal-polymer electrodes
The Fraunhofer Institute for Electron Beam and Plasma Technology (FEP) sees its results as “valuable basis for optimizing lithium-ion batteries” in industry. According to Fraunhofer FEP, the technology developed by its researchers enables “the precise application of copper and aluminum layers onto polymer films to produce current collectors with electrical conductivity and thickness comparable to conventional metal foil-based current collectors.” While current collectors are also simply referred to as electrodes, Fraunhofer FEP consistently uses the term ‘current collectors’ in its announcement.
Battery electrodes are produced by coating the active materials (such as a lithium, nickel, manganese, cobalt and binder mixture in an NMC cathode) onto a thin metal foil. This metal foil – typically aluminium for the cathode and copper for the anode – serves as the carrier, while the electrochemical reaction for energy storage takes place on the coating surface. The innovation here focuses precisely on replacing these carrier foils inside the electrodes.
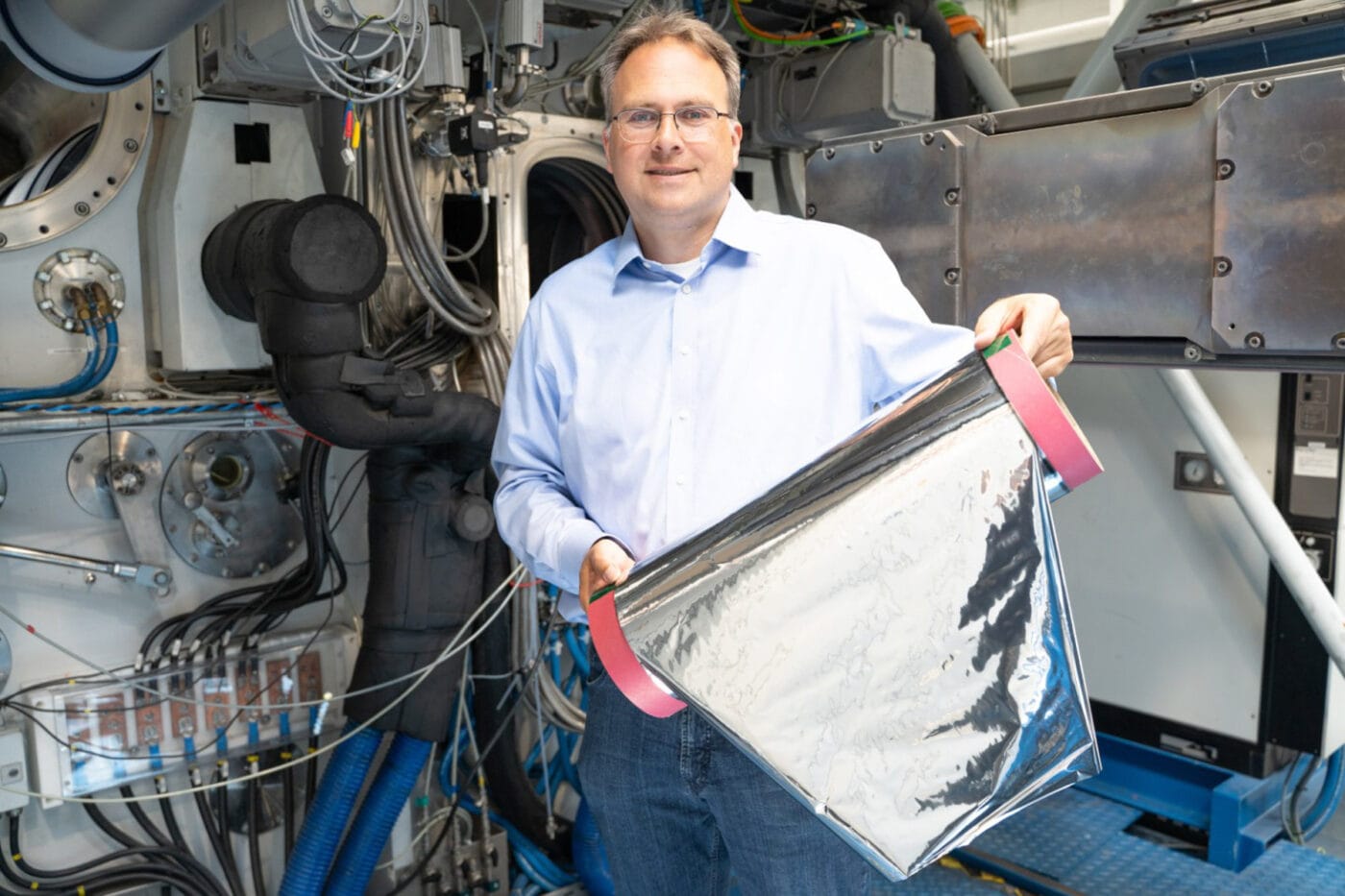
The research team in Dresden has substituted the pure metal foil with a polymer film coated on both sides with a thin layer of aluminium or copper – offering similar conductivity properties to pure metal foils. Both copper and aluminium coatings are around one micrometre thick. According to Fraunhofer FEP, the coated polymer films remained “free of significant wrinkling – ideal for further processing in battery production.” The coatings themselves were applied using electron beam evaporation.
“The challenge was to design the polymer films and the coating process in such a way that the thickness of the current collector could be comparable to that of current metal films and the metal layer could have optimum electrical conductivity,” says technical project manager Claus Luber. The team succeeded and demonstrated the deposition of thick copper and aluminium layers onto 12-micrometre PET films. Deposition was carried out in a roll-to-roll process on web widths up to 60 centimetres.
Polymer films offer two main advantages. Firstly, they are lighter than pure metal foils due to the ultra-thin metal coating of just one micrometre per side. This reduces electrode weight and increases the battery cell’s energy density. More importantly, however, is the safety aspect. Should an internal short circuit occur, the polymer substrate melts, interrupting the current path. “ This prevents heat from continuing to build up and causing thermal runaway,” explain the researchers.
In the PolySafe project funded by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), the team demonstrated not only the production process but also a functional cell based on these electrodes. Project partner TU Braunschweig manufactured pouch cells using the metal-polymer current collectors. “These cells were tested for their electrochemical properties and compared with conventional reference cells. In these tests, the cells with metal-on-polymer current collectors performed similarly to the reference cells in terms of performance and cycle stability at different charging and discharging rates,” reports Fraunhofer FEP.




0 Comments